ChimeraX Recipes
Move a surface to highest intensity in 3D microscope image
A fluorescently labeled membrane will be seen in 3D microscopy with a thickness that is much greater than the actual membrane due to limited microscope resolution. Here is a ChimeraX command that tries to place a surface at the highest intensity in the middle of the shell seen in a 3D microscope image. It starts with surfaces at a specified intensity level (an isosurface). That will show inner and outer surfaces of the shell. The command moves those surfaces toward higher intensity following the intensity gradient.
To define the midsurf command open the Python code midsurf.py with ChimeraX command
open midsurf.py
And here is an example opening a 3-channel 3D microscope image cell14.tif and moving the isosurfaces for channel 1.
open cell14.tif
volume #1.1 level X
midsurf #1.1
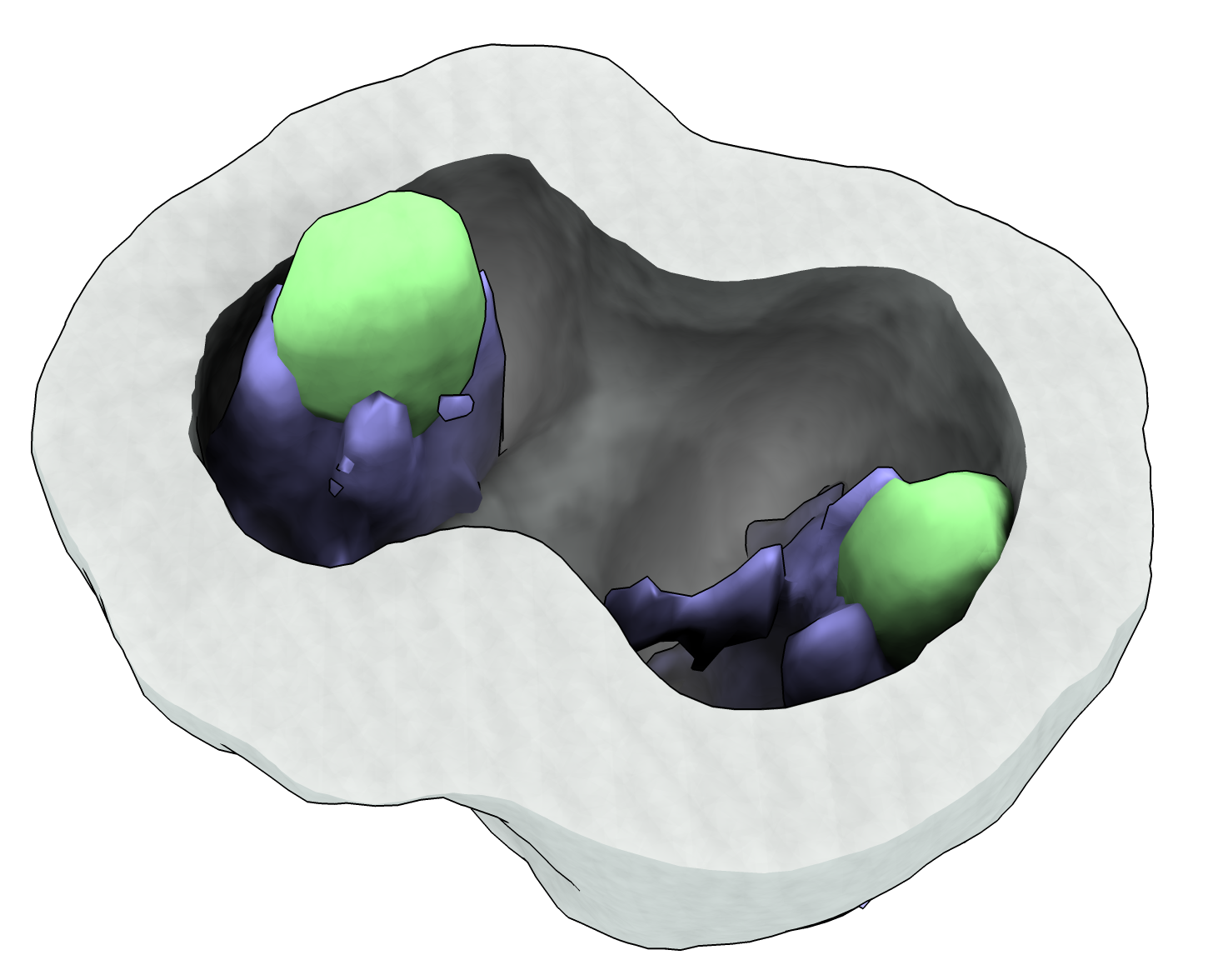
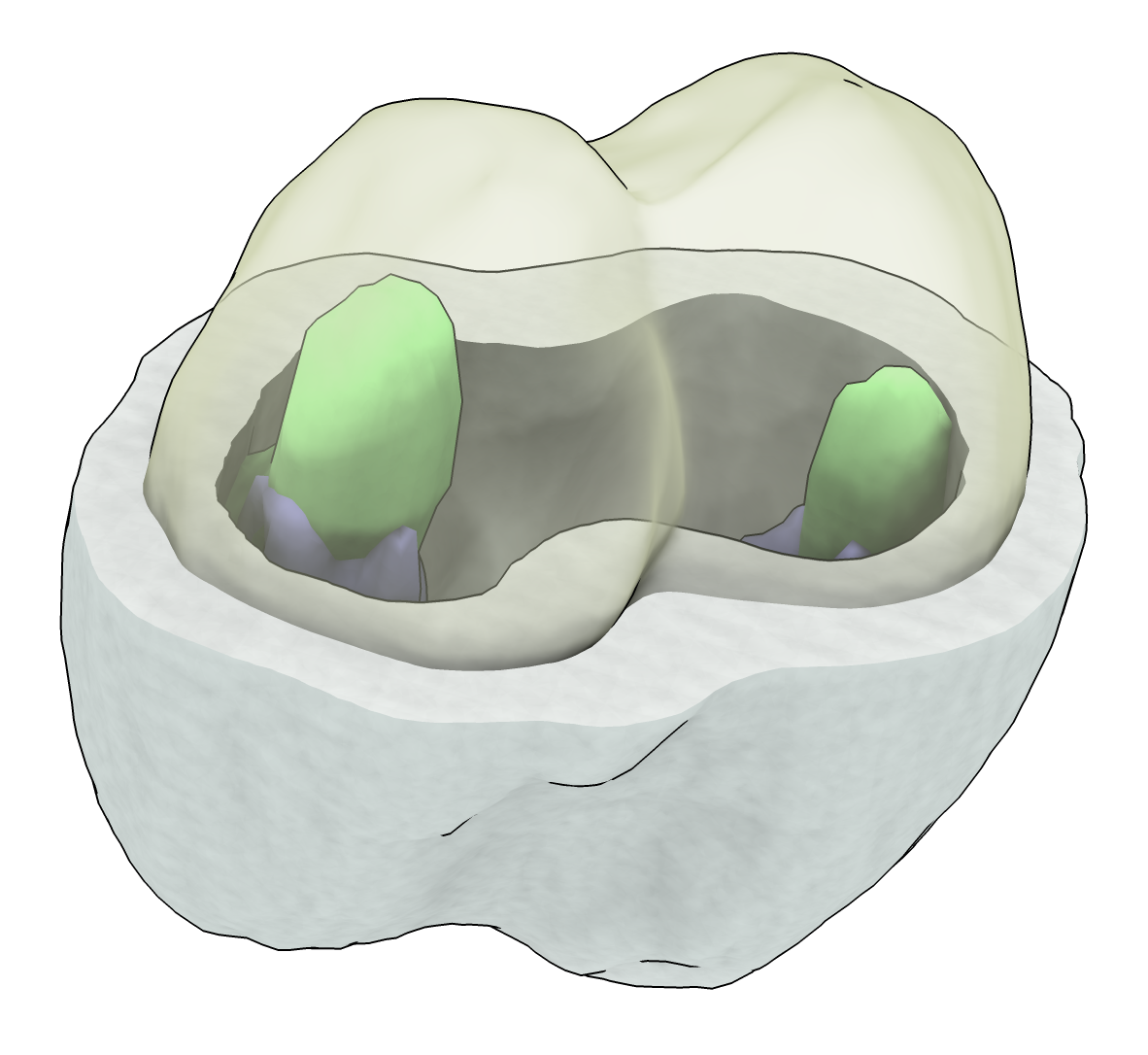
The midsurf command can be run multiple times until it the surface coverges to the highest intensity position. The first image shows the cell with the membrane cut in half, and the second image shows the computed middle surface in transparent yellow.
 |
 |
More Options
The midsurf command has several additional options
midsurf #2 volume #1 steps 100 voxelStep 0.1 smoothingIterations 1 smoothingFactor 0.1
You can specify an initial surface to move (#2 in the example) that is not a map isosurface and then you also need to specify the map (“volume #1” in the example). The motion is done in steps, by default 100 steps, each step moving at most a certain fraction of the grid spacing (voxelStep 0.1) perpendicular to the surface. To avoid creases in the surface the vertices are also moved toward the average of the neighbor vertices at each step. That smoothing is does some number of iterations (smoothingIterations 1) moving each vertex a fraction of the way (smoothingFactor 0.1) to the average neighbor position. The smoothing can make the surface smaller, contracting a spherical surface, and can pull the surface away from the intensity maximum. It is useful to try “smoothingIterations 0” after the surface is moved to see if it changes the position.
Surface Coloring
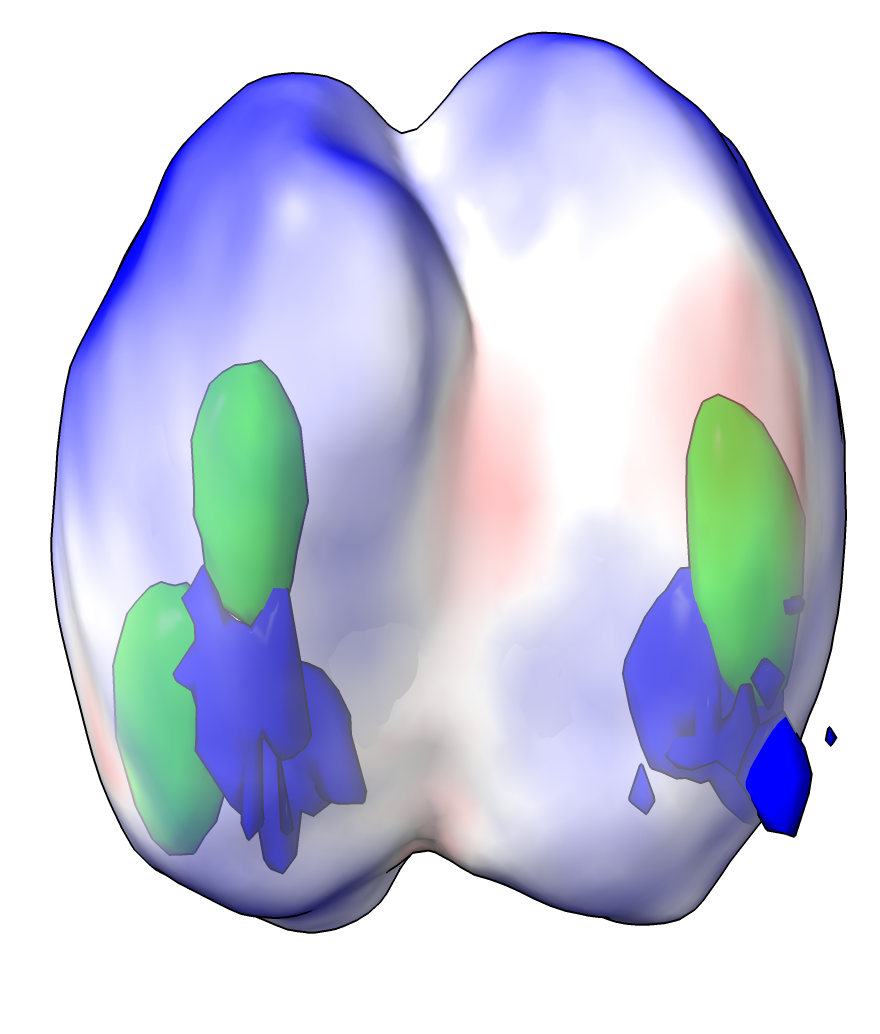
The middle surface can be colored according to the image intensity using menu Tools / Volume Data / Surface Color or the equivalent command
color sample #1.1 map #1.1 palette bluered
transparency #1.1 50
Here is the Python code midsurf.py
# Move surface vertices along a volume gradient until they reach a maximum.
# Move them normal to the surface and keep the vertices and normals uniform
# by smoothing frequently.
#
# This is to find the center cell membrane surface in a roughly spherical shell
# seen in light microscopy. For Arthur Charles-Orszag.
#
def middle_surface(session, surface, volume = None, steps = 100, voxel_step = 0.1,
smoothing_factor = 0.1, smoothing_iterations = 1):
from chimerax.map import VolumeSurface
if volume is None and isinstance(surface, VolumeSurface):
volume = surface.volume
points = surface.vertices
xyz_to_ijk_transform = volume.data.xyz_to_ijk_transform * volume.scene_position.inverse() * surface.scene_position
data_array = volume.full_matrix()
gradients = points.copy()
max_step = min(volume.data.step) * voxel_step
from chimerax.map_data import interpolate_volume_gradient
vertices, normals, triangles = surface.vertices, surface.normals, surface.triangles
for step in range(steps):
interpolate_volume_gradient(vertices, xyz_to_ijk_transform, data_array,
gradients = gradients)
ips = (normals * gradients).sum(axis = 1)
mag = max(abs(ips.max()), abs(ips.min()))
ips *= max_step / mag
vertices += normals*ips[:,None]
from chimerax.surface import smooth_vertex_positions
smooth_vertex_positions(vertices, triangles, smoothing_factor, smoothing_iterations)
from chimerax.surface import calculate_vertex_normals
normals = calculate_vertex_normals(vertices, triangles)
surface.set_geometry(vertices, normals, triangles)
def register_command(logger):
from chimerax.core.commands import CmdDesc, register, SurfaceArg, IntArg, FloatArg
from chimerax.map import MapArg
desc = CmdDesc(
required = [('surface', SurfaceArg)],
keyword = [('volume', MapArg),
('steps', IntArg),
('voxel_step', FloatArg),
('smoothing_factor', FloatArg),
('smoothing_iterations', IntArg)],
synopsis = 'Move surface to volume maxima'
)
register('midsurf', desc, middle_surface, logger=logger)
register_command(session.logger)
Tom Goddard, December 1, 2022